Key Takeaways
- Lean principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and continuous improvement.
- They guide teams to reduce waste and focus on value.
- Tools like Kanban, 5 Whys, and Kaizen reinforce those principles.
- Real success depends on culture: shared leadership, respect, and adaptability.
- With the right software and mindset, Lean drives measurable results across industries.
Lean is a proven approach for building efficient, customer-focused teams. Rooted in the Toyota Production System (TPS), it has evolved into a universal framework adopted across industries - manufacturing, software development, healthcare, and more. By focusing on eliminating waste and improving workflows, Lean helps organizations deliver better results with fewer resources.
What Are the 5 Lean Principles?
The five key Lean management principles of building an efficient process are:
1. Identify Value: Determine what customers truly need and eliminate unnecessary work.
2. Map the Value Stream: Visualize how work flows through the process to deliver value.
3. Create a Flow: Ensure work moves smoothly without delays or bottlenecks.
4. Establish a Pull System: Produce only what is needed, when it’s needed, to avoid overproduction.
5. Seek Continuous Improvement: Continuously refine processes to boost efficiency and adaptability.
 The five Lean management principles
The five Lean management principles
Principle 1: Identifying Value
Value is defined by what your customer is willing to pay for. Every team should understand what value they provide, whether it's customer-facing or internal. For example, a QA team may not deliver direct value to a customer, but plays a vital role in ensuring the end product meets quality expectations.
Lean distinguishes between:
-
Necessary waste: Non-value-adding but required (e.g., testing).
-
Pure waste: Non-essential activities that should be removed.
By identifying value, you begin to focus your efforts on what matters most.
Principle 2: Mapping the Value Stream
Mapping the value stream reveals how work moves through your process and highlights where waste occurs. One of the most effective tools for this is the Kanban board. A basic version includes three columns:
- Requested
- In Progress
- Done
You can expand these columns to reflect more detailed stages relevant to your workflow, like "Ready to Start," "Design," "Review," etc. This visibility makes it easier to identify and eliminate steps that don't add value.
 Example of a basic Kanban board with 3 columns: Requested, In Progress, and Done
Example of a basic Kanban board with 3 columns: Requested, In Progress, and Done
Principle 3: Creating a Flow
In Lean management, flow refers to the smooth movement of tasks from start to finish. Disruptions - like bottlenecks or waiting for approvals - slow down delivery. To improve flow:
-
Remove bottlenecks or prevent them from becoming overloaded.
-
Limit work in progress (WIP) to prevent multitasking and reduce delays.
-
Encourage team discussions to set clear WIP limits.
-
Reduce context switching for more focused execution.
These practices help maintain a consistent pace and improve team efficiency.
 Identifying a workflow process bottleneck
Identifying a workflow process bottleneck
10 Years Kanban Experience In 1 Free Book.
Project Manager's Guide to Kanban
Principle 4: Establishing a Pull System
A pull system means teams only begin work when there's demand and capacity. This contrasts with push systems, where work is assigned regardless of team readiness, often causing overload.
Pull systems:
- Prevent overproduction
- Prioritize high-impact tasks
- Support better workload balance
Track progress with key metrics:
-
Cycle time: How long it takes to complete a task
-
Throughput: Number of tasks completed in a timeframe
Shorter cycle times and improved throughput are signs of a healthy pull system.
 Pull system production vs. push production
Pull system production vs. push production
Principle 5: Seeking Constant Improvement
Improvement isn't a one-time effort - it's a mindset. Lean encourages regular reflection and adaptation. Implement practices like:
-
PDCA cycles: The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a proven method for driving continuous improvement.
-
Daily stand-ups: Quick syncs to review progress and blockers.
-
Empowered teams: Give people ownership of problem-solving.
-
Learning culture: Encourage feedback, experimentation, and iteration.
Over time, continuous improvement becomes an integral part of your team's culture.
How the Lean Principles Improve Organizational Performance
Implementing Lean improves:
-
Efficiency: Less time wasted on non-essential tasks
-
Agility: Teams can pivot faster
-
Customer satisfaction: Focus remains on what users actually want
Teams using Lean report better collaboration, faster delivery, and higher morale, especially when continuous improvement and respect for people are part of the culture.
How the Lean Principles Help Eliminate Waste and Improve Flow
By mapping the value stream and analyzing how work moves through your system, Lean exposes inefficiencies like:
- Rework
- Overprocessing
- Delays due to approvals or unclear ownership
Using tools like Kanban boards, you can visualize each process step - from "Requested" to "Done" - and continuously refine it. Simple tweaks, such as splitting "In Progress" into stages (e.g., design, test, review), help uncover delays and optimize the flow.
What Cultural Shifts Are Needed to Succeed with Lean?
Lean isn't just about tools - it's a mindset. Success depends on these cultural values:
-
Respect for people: Empower individuals to solve problems.
-
Shared leadership: Flatten hierarchies and trust teams.
-
Transparency: Visualize progress and identify blockers together.
-
Learning: Encourage experimentation, feedback, and growth.
-
Daily check-ins and PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycles reinforce a culture of constant progress.
Implementing the Lean Principles
Here's a simplified path:
-
Define your value: What do customers truly need?
-
Map your value stream: Use visual tools to analyze current workflows.
-
Start small: Pilot Lean in one department.
-
Establish feedback loops: Use retrospectives, reviews, and data.
-
Scale and adapt: Expand Lean gradually, supported by leadership and change agents.
Key Challenges in Implementing Lean
Despite its benefits, Lean adoption can fail due to:
-
Resistance to change: Teams may fear loss of control or stability.
-
Poor communication: Misalignment between leadership and teams.
-
Lack of clarity: Teams need a clear "why" behind the shift.
-
Tool overuse: Applying Lean tools without understanding the mindset.
Start small, focus on one team or department, and scale based on success. Appoint Lean champions to lead the shift.
What Are the Best Lean Software Tools for Waste Elimination?
To implement Lean effectively, consider tools that support practices and techniques that help visualize and optimize workflows, including:
- Value stream mapping
- Kanban boards
- Custom WIP limits
- Cycle time analytics
- PDCA templates
Businessmap, Planview's AgilePlace, and Jira Align are popular platforms that offer trial periods or demos for teams adopting Lean.
By applying these Lean principles, your organization can work smarter - not just harder - and continuously adapt to deliver better results with less waste.
Businessmap is the most flexible software
to align work with company goals
In Summary
- What are the 5 Lean principles? Identify value, map the value stream, create flow, establish a pull system, and seek continuous improvement.
- What are the 3 core concepts of Lean? Create value for the customer, eliminate waste, and continuously improve.
- What are the 2 key pillars of Lean? Respect for people and continuous improvement. Trust, ownership, and collaboration are essential for building a high-performing Lean team.





 The five Lean management principles
The five Lean management principles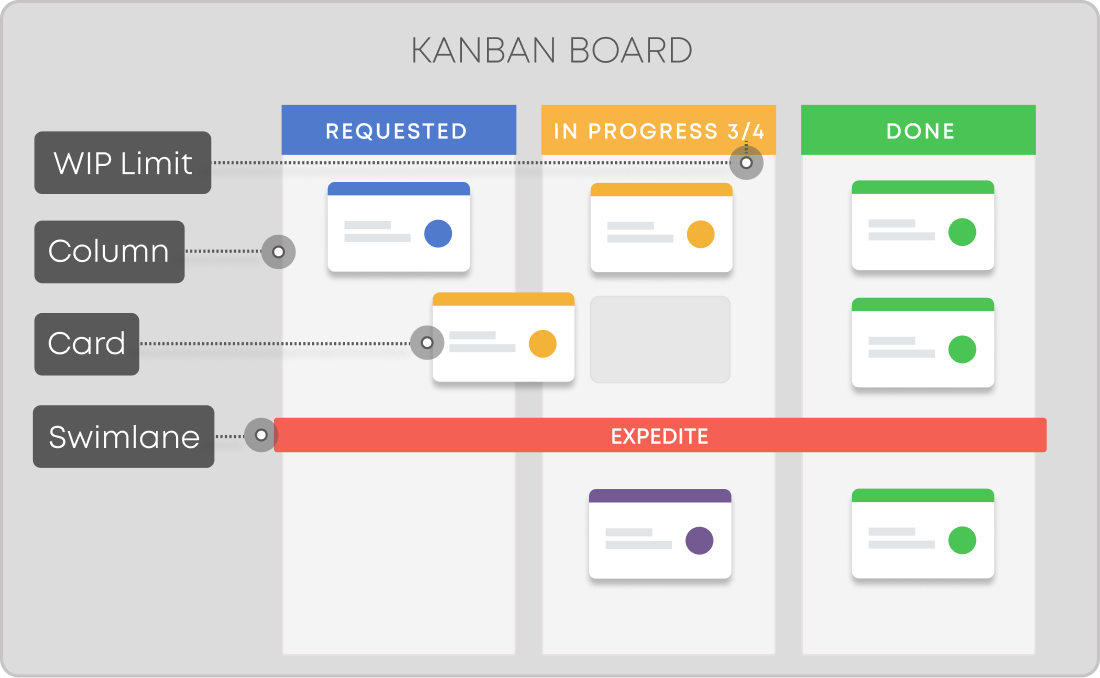 Example of a basic Kanban board with 3 columns: Requested, In Progress, and Done
Example of a basic Kanban board with 3 columns: Requested, In Progress, and Done Identifying a workflow process bottleneck
Identifying a workflow process bottleneck
 Pull system production vs. push production
Pull system production vs. push production 


