Enterprise workflow management is a critical aspect of modern business operations, yet many organizations struggle to understand and effectively implement it fully. In today's fast-paced and constantly evolving corporate landscape, efficient and streamlined workflows are essential for success.
However, with the increasing complexity of business processes, manual management of workflows is no longer sufficient. This is where enterprise workflow management comes into play. But what exactly is enterprise workflow management? How can it be implemented within an organization? And what solutions are available to facilitate its effective use?
In this article, we delve into the core concepts, explore seamless implementation strategies, and unveil cutting-edge solutions to streamline your business process management practices.
What Is a Workflow?
A workflow is a systematic and repeatable sequence of actions designed to achieve a particular business objective. It is a structured process where tasks are organized and executed in a procedural manner to accomplish a specific goal efficiently.

Workflows are characterized by their reliability and consistency, as they provide a clear pathway for completing tasks or activities within a given context. Workflows have a cyclic nature, where the defined set of actions can be executed over and over again to achieve the desired outcome.
What Is Enterprise Workflow Management?
Enterprise workflow management refers to the comprehensive oversight and optimization of numerous processes that are integral to the functioning of large organizations. It involves a systematic examination of the myriad tasks and operations that different departments and teams within an enterprise undertake to ensure smooth and efficient functioning.

The goal of enterprise workflow management is to enhance overall organizational efficiency by identifying, streamlining, and improving the various workflows that contribute to the success of the enterprise.
What Are the Different Types of Enterprise Workflows?
Let’s explain the three different types of enterprise workflows that an organization can have.
Further, you can read more about the difference between workflow and process.
Process Workflows
-
Definition: Process workflows are characterized by their repeatability, where the steps and tasks that constitute the workflow are predictable.
-
Repeatable Nature: A workflow is considered repeatable if it consistently produces the same output, with minimal variations, when given the same input.
-
Predictable Tasks: The tasks within a process workflow are predictable, and the process involves clearly defining when a specific task needs to be performed, which tasks are to be performed next, and identifying the responsible person or team/department for each task.
Project Workflows
-
Definition: Project workflows are non-repeatable, meaning they exhibit variations in output even when given the same input.
-
Predictable Tasks: Similar to process workflows and based on the nature of the work at hand, project workflows could also involve predictable tasks or steps.
-
Reusable Elements: While individual projects may not be exactly the same, elements or the entire workflow of a project can be reused when initiating new projects.
Case Workflows
-
Definition: Case workflows are both non-repeatable and unpredictable. The tasks or steps required are not initially known and only become apparent after gathering more information about the workflow.
-
Non-Predictable Steps: In the case of workflow, the initial steps required to fulfill the workflow are not known until more information is gathered, making it non-predictable.
-
Problem-Solving Nature: Case workflows often involve handling problems that require specific and unique solutions.
How to Build Your Enterprise Workflows: Our Step-by-Step Approach
Let’s outline the different phases or elements of Enterprise Workflow Management (EWM):
Step 1. Identify Workflows
-
What to Do: This initial phase involves recognizing and listing all the workflows within the enterprise. It acknowledges that in complex organizational settings, workflows might not always be immediately apparent and may need thorough identification.
-
Complexity Consideration: Recognizes the potential complexity, with an enterprise possibly having tens or even hundreds of workflows.
-
Prioritization Challenge: Highlights the challenge of prioritizing which workflows to analyze and optimize in subsequent phases.
Step 2. Map Workflows
-
What to Do: After identification, the next phase is to map the workflows visually using techniques such as flowcharts.
-
Visualization Formats: Workflow diagrams can be visualized in an as-is format, reflecting the current execution, or as a to-be format, representing the ideal and optimized form of the workflow.
-
Objectives: Aim to standardize the understanding of workflows across different stakeholders and provide a basis for subsequent analysis and optimization.
Step 3. Analyze Enterprise Workflow
-
What to Do: Once mapped, the organization analyzes the performance of the workflows to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
-
Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: Involves measuring quantitative metrics and analyzing qualitative data gathered through observation, stakeholder interviews, and other methods.
-
Alignment with Objectives: Emphasizes the importance of measuring the workflow's performance against the broader objectives of the enterprise.
Step 4. Optimize Workflows
-
What to Do: This phase involves implementing changes based on the analysis conducted in the previous phase. The goal is to eliminate inefficiencies, address bottlenecks, and enhance the overall efficiency of specific tasks or the entire workflow.
-
Automation Consideration: Acknowledges that, if viable, automation may be implemented to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and consistency.
Step 5: Evaluate Workflow
-
What to Do: The final phase emphasizes the continuous nature of EWM. It involves monitoring and evaluating the optimized workflows over time.
-
Changing Dynamics: Recognizes that a workflow's efficiency may change over time due to factors such as the introduction of new tools, equipment, competitive advancements, etc.
-
Stakeholder Involvement: Stresses the importance of involving stakeholders regularly to gather feedback and ensure ongoing improvement.
Why Do You Need Enterprise Workflow Management Solutions?
Enterprise Workflow Management (EWM) is crucial for several reasons:
-
Reduced Errors: EWM, particularly workflow mapping, enables standardization, leading to consistency and accuracy. This results in a significant reduction in errors during workflow execution.
-
Enterprise Flexibility and Agility: Well-mapped and documented workflows provide flexibility for implementing changes in the enterprise. EWM enhances the organization's agility, making it more competitive, flexible, and scalable in today's dynamic market.
-
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Through continuous analysis and monitoring, EWM identifies inefficiencies and bottlenecks, leading to optimized workflows and increased efficiency and productivity.
-
Data Accuracy: EWM ensures the accuracy of data management by providing a more precise overview of how workflows must be executed.
-
Compliance Maintenance: EWM allows businesses to streamline and standardize workflows, ensuring compliance with internal and external regulations and policies. Guidelines can be quickly implemented and documented within the workflow.
-
Data Security and Authorization: EWM enhances data management accuracy and security. By providing an accurate overview of workflow execution, it enables precise control over data access, authentication, and authorization, ensuring confidentiality and compliance.
How Can Businessmap Enhance Your Enterprise Workflow Management?
Businessmap’s enterprise workflow management software offers a comprehensive solution for enhancing enterprise workflow management. Here are some ways in which our enterprise software can benefit your organization:
Strategic Alignment
-
Connect Strategy with Execution: The software allows you to align your business strategy with day-to-day execution. This ensures that your workflows are in sync with your long-term objectives. Visualize and connect objectives and key results (OKRs) across the entire enterprise, from C-level executives to team management.
-
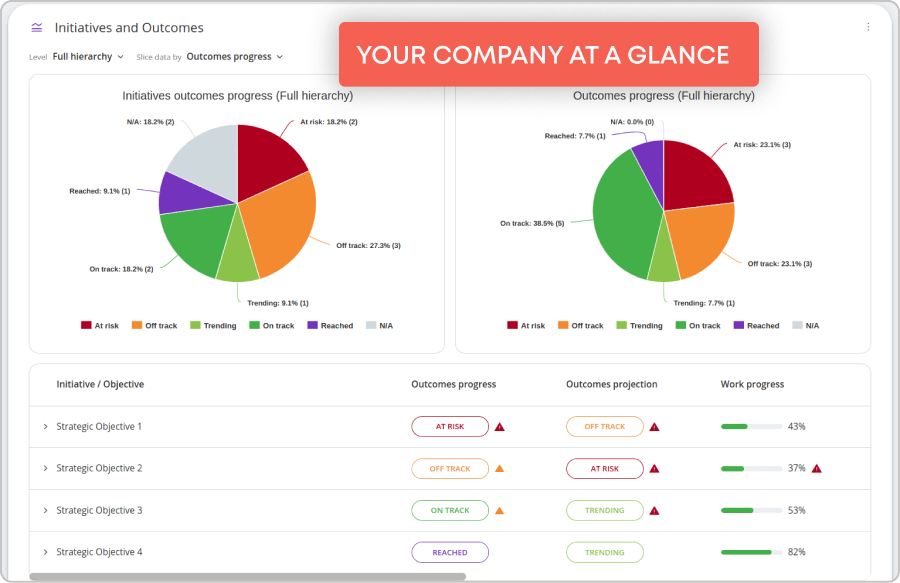
Centralized Objectives Monitoring: Executive dashboards provide a centralized view of all business objectives supporting different workflows, which enables real-time monitoring, risk detection, and data aggregation at a departmental level.

Work Management
-
Streamlined Project Portfolio Management: The software streamlines project portfolio management by making your project workflows transparent. This allows managers to see their work initiatives at a glance and focus on the most critical things. Visualization works both on project and daily work management levels, connecting all work processes across the enterprise.
-
Data-Driven Management: Embrace data-driven decision-making by gaining instant insights into performance metrics. Historical data and project delivery forecasts contribute to informed decision-making.
Security
-
Enterprise-Grade Security: The software provides robust security features, including single sign-on (SSO), two-factor authentication (2FA), data encryption at rest, multi-region data centers, IP whitelisting, and strong password policies. This ensures the safety of your enterprise data.
Controls
-
Account Management with Controls and Permissions: The software facilitates easy account management with controls and custom permissions.
-
Admin Privileges: Grant specific privileges to administrators and define custom roles and permissions for different users.
-
Security Controls: Implement various security controls, including card controls, custom teams, and audit logs, to enhance overall security.
-
Workspace Management: Effectively manage workspaces within the software environment.
Support and Onboarding
-
Enterprise-Level Onboarding: Dedicated customer success managers are provided as part of enterprise-level onboarding. They guide you through implementation, training sessions, and data migration, ensuring a smooth setup.
-
Implementation Flexibility: The software offers flexible implementation options, including self-service, guided, or professional services, catering to diverse organizational needs.
Overall, the Businessmap Enterprise Software aims to optimize processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and facilitate effective decision-making by providing a centralized platform for strategic alignment and a secure work management environment.
Businessmap is the most flexible software
to align work with company goals
In Summary
Mastering Enterprise Workflow Management (EWM) is pivotal for organizations aiming to boost efficiency and streamline operations. This concise overview encapsulates the essence of EWM and provides key takeaways for a successful implementation.
- By establishing clear workflows and utilizing automation and tracking tools, organizations can increase efficiency, productivity, and, ultimately, profitability.
- To successfully implement enterprise workflow management, it is important to involve all stakeholders, thoroughly analyze and map out existing processes, and continuously monitor and adapt to any changes.
- With a well-executed workflow management strategy, businesses can stay competitive and achieve long-term success in today's fast-paced and ever-changing market.